Computer Network by Tanenbaum¶
ch1¶
term¶
broadcast
广播
point-to-point link
单播
multicasting
组播:只对一部分用户发送
- physical layer
- data link layer
- 数据链路层。传输数据帧
- 为了控制通路,有时需要 介质控制子层 medium access control layer
- network layer
- transport layer
- 传输层。主要负责向两个主机中进程之间的通信提供服务。TCP 协议
- application layer
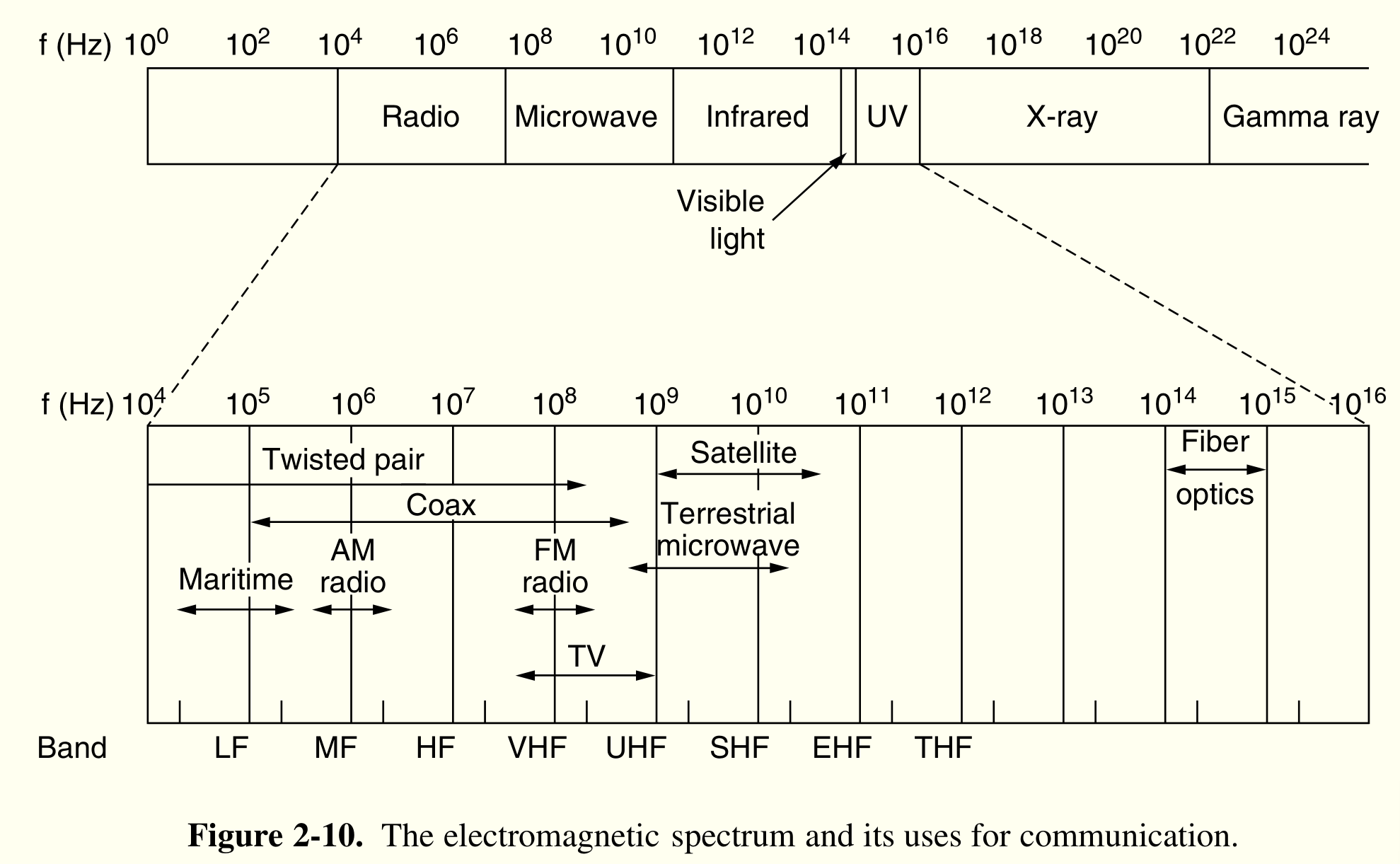
ch2 物理层¶
SNR
Signal-to-Noise Ratio,信噪比,dB(分贝)单位($10\log_{10}S/N$)
信道容量¶
$$\text{maximum data rate} = 2B \log_2 V \rm{bits/sec}$$
$$\text{maximum number of bits/sec} = B \log_2(1 + S/N)$$
- 双绞线,几公里级,电话线,cat567
- 同轴电缆,Cu 制
- 光纤,带宽高,损失少
- 无线通信
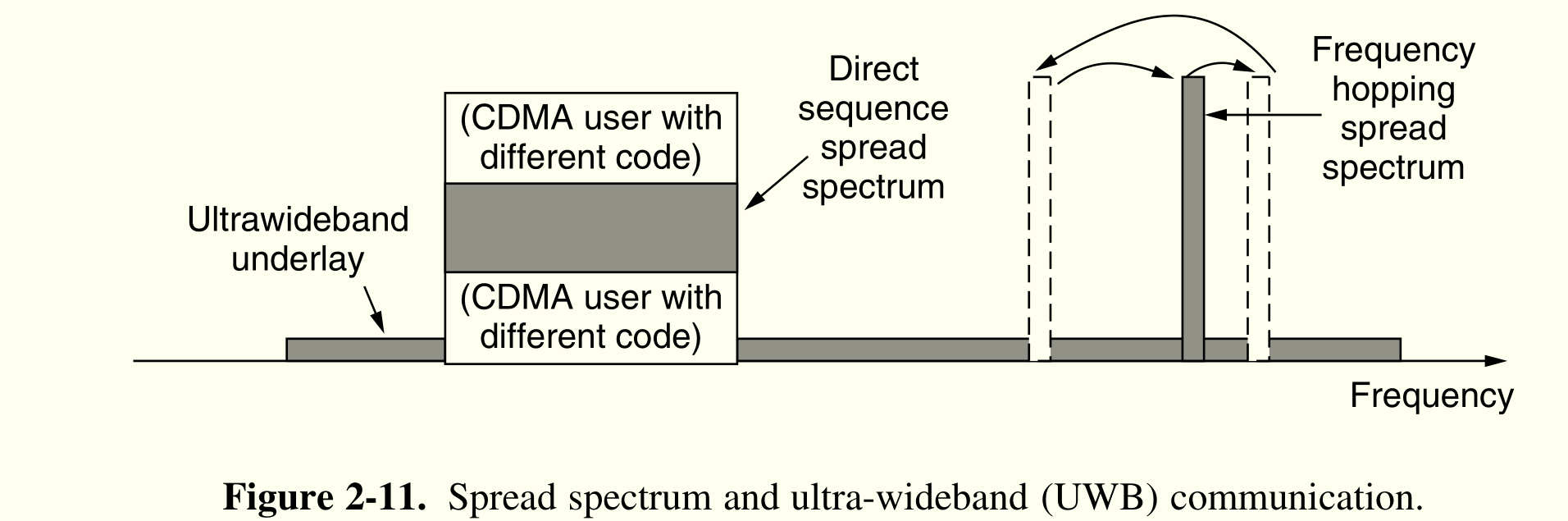
- 一般使用单一窄频段( $\Delta f/f\ll 1$ )
- 跳频 frequency hopping spread spectrum
- CDMA 码分多址,Code Division Multiple Access
- FDM 频分复用,Frequency Division Multiplexing ^67f4ec
- TDM 时分复用,Time Division Multiplexing
- UWB 超宽频谱,Ultra-WideBand
- RF
- 低频高 path loss, $1/r^2$ 损失,地波 VLF,LF,MF
- 高频直线,损失少,电离层反射 HF,VHF
ch3 数据链路层¶
- 为网络层提供接口
- 检错纠错
- 调节数据流量,防止堵塞
在 数据链路层 完成检错、确认等比起在网络层,更快速,更加底层。
frame¶
从原始 bit 区分 frame。一般使用字符计数法和一种其它方法的组合
- bit 计数,若出错,对帧的影响较大
- flag byte,填充 byte
- flag bit,填充 bit
- 直接违反物理层编码,只适用于物理层编码有冗余的网络
检错纠错¶
$(n,m)$ 码,当中 $n=m+r$
- hamming
- 二进制卷积
- solmen Reed
- 低密度奇偶校验
hamming¶
Hamming distance
海明距离,两个码字之间不同的对应比特位数目
为了检查出 $d$ 个 bit 错,可以使用海明距离为 $d+1$ 的编码;为了纠正 $d$ 个错,可以使用海明距离为 $2d+1$ 的编码
对 $2^m$ 个有效信息(信息位数为 $m$ )中任何一个,有 $n=m+r$ 个与其距离为 1 的无效码字(n 位每位都可能出错),因此,每个 $2^m$ 中的合法消息需要 $n+1$ 个位模式来标识它们。有 $(n+1)2^m\le2^n$ ,或者是
$$(m+r+1)\le2^r$$
给定 $m$ ,利用该式可以得出校正单比特误码的校验位数目的下界。可采用 k 个码字组成 $k\times n$ 矩阵,按列发送,接收方恢复成 $k\times n$ 矩阵。$kr$个校验位, $km$ 个数据位,可纠正最多为 k 个的突发性连续比特错
protocol¶
- 传输层协议 TCP 也提供可靠传输服务
- 链路层的可靠传输服务通常用于高误码率的连路上,如无线链路
- 对于误码率低的链路,链路层协议可以不实现可靠传输功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| #define MAX_PKT 1024 /* determines packet size in bytes */
typedef enum {false, true} boolean;/* boolean type */
typedef unsigned int seq_nr;/* sequence or ack numbers */
typedef struct {unsigned char data[MAX_PKT];} packet;/* packet definition */
typedef enum {data, ack, nak} frame_kind;
/* frame kind definition */
typedef struct {
/* frames are transported in this layer */
frame_kind kind;
/* what kind of frame is it? */
seq_nr seq;
/* sequence number */
seq_nr ack;
/* acknowledgement number */
packet info;
/* the network layer packet */
} frame;
/* Wait for an event to happen; return its type in event. */
void wait_for_event(event_type *event);
/* Fetch a packet from the network layer for transmission on the channel. */
void from_network_layer(packet *p);
/* Deliver information from an inbound frame to the network layer. */
void to_network_layer(packet *p);
/* Go get an inbound frame from the physical layer and copy it to r. */
void from_physical_layer(frame *r);
/* Pass the frame to the physical layer for transmission. */
void to_physical_layer(frame *s);
/* Start the clock running and enable the timeout event. */
void start_timer(seq_nr k);
/* Stop the clock and disable the timeout event. */
void stop_timer(seq_nr k);
/* Start an auxiliary timer and enable the ack_timeout event. */
void start_ack_timer(void);
/* Stop the auxiliary timer and disable the ack_timeout event. */
void stop_ack_timer(void);
/* Allow the network layer to cause a network layer ready event. */
void enable_network_layer(void);
/* Forbid the network layer from causing a network layer ready event. */
void disable_network_layer(void);
/* Macro inc is expanded in-line: increment k circularly. */
#define inc(k) if (k < MAX_SEQ) k = k + 1; else k = 0
|
1 帧包含 4 个字段:
- kind:种类:控制信息帧还是数据帧
- seq:帧序号
- ack:回应
- info:数据
乌托邦式的单工协议¶
单边发送,单边接收。发送方和接收方的网络层总是处于准备就绪状态。数据处理的时间忽略不计。可用的缓存空间无穷大。最强的一个条件是数据链路层之间的通信信道永远不会损坏帧或者丢失帧。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| /* Protocol 1 (Utopia) provides for data transmission in one direction only, from
sender to receiver. The communication channel is assumed to be error free
and the receiver is assumed to be able to process all the input infinitely quickly.
Consequently, the sender just sits in a loop pumping data out onto the line as
fast as it can. */
typedef enum {frame_arrival} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
void sender1(void)
{
frame s;
/* buffer for an outbound frame */
packet buffer;
/* buffer for an outbound packet */
while (true) {
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* go get something to send */
s.info = buffer;
/* copy it into s for transmission */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* send it on its way */
}
/* Tomorrow, and tomorrow, and tomorrow,
Creeps in this petty pace from day to day
To the last syllable of recorded time.
– Macbeth, V, v */
}
void receiver1(void)
{
frame r;
event_type event;
/* filled in by wait, but not used here */
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* only possibility is frame_arrival */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* go get the inbound frame */
to_network_layer(&r.info);
/* pass the data to the network layer */
}
}
|
简单的 停-等 协议,无错信道¶
stop-and-wait
发送方在接收方确认接受前,都等待的协议,用于流量控制
双方交替发 frame,每个 frame 中含有上个 frame 的确认信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| /* Protocol 2 (Stop-and-wait) also provides for a one-directional flow of data from
sender to receiver. The communication channel is once again assumed to be error
free, as in protocol 1. However, this time the receiver has only a finite buffer
capacity and a finite processing speed, so the protocol must explicitly prevent
the sender from flooding the receiver with data faster than it can be handled. */
typedef enum {frame_arrival} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
void sender2(void)
{
frame s;
/* buffer for an outbound frame */
packet buffer;
/* buffer for an outbound packet */
event_type event;
/* frame_arrival is the only possibility */
while (true) {
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* go get something to send */
s.info = buffer;
/* copy it into s for transmission */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* bye-bye little frame */
wait_for_event(&event);
/* do not proceed until given the go ahead */
}
}
void receiver2(void)
{
frame r, s;
/* buffers for frames */
event_type event;
/* frame_arrival is the only possibility */
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* only possibility is frame_arrival */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* go get the inbound frame */
to_network_layer(&r.info);
/* pass the data to the network layer */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* send a dummy frame to awaken sender */
}
}
|
简单的 停-等 协议,信道可能出错¶
- 需要加入计时器,防止 frame 丢失
- 需要标记帧号码,防止重复接收
考虑 $m$ 帧和 $m+1$ 帧。如果 $m$ 帧没有发送成功,接收方不会确认;如果发送成功,接收方就会发确认消息。所以下一次发送方要么重发 $m$ 帧,要么接收到正确的确认消息,发 $m+1$ 帧。所以每次只需要区分 2 帧,帧号码只需要 1 位(单 bit)
PAR (Positive
Positive Acknowledgement with Retransmission,带有重传的肯定确认
ARQ
Automatic Repeat reQuest,自动重复请求
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| /* Protocol 3 (PAR) allows unidirectional data flow over an unreliable channel. */
#define MAX_SEQ 1
/* must be 1 for protocol 3 */
typedef enum {frame_arrival, cksum_err, timeout} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
void sender3(void)
{
seq_nr next_frame_to_send;
/* seq number of next outgoing frame */
frame s;
/* scratch variable */
packet buffer;
/* buffer for an outbound packet */
event_type event;
next_frame_to_send = 0;
/* initialize outbound sequence numbers */
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* fetch first packet */
while (true) {
s.info = buffer;
/* construct a frame for transmission */
s.seq = next_frame_to_send;
/* insert sequence number in frame */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* send it on its way */
start_timer(s.seq);
/* if answer takes too long, time out */
wait_for_event(&event);
/* frame_arrival, cksum_err, timeout */
if (event == frame_arrival) {
from_physical_layer(&s);
/* get the acknowledgement */
if (s.ack == next_frame_to_send) {
stop_timer(s.ack);
/* turn the timer off */
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* get the next one to send */
inc(next_frame_to_send);
/* invert next_frame_to_send */
}
}
}
}
void receiver3(void)
{
seq_nr frame_expected;
frame r, s;
event_type event;
frame_expected = 0;
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* possibilities: frame_arrival, cksum_err */
if (event == frame_arrival) {
/* a valid frame has arrived */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* go get the newly arrived frame */
if (r.seq == frame_expected) {
/* this is what we have been waiting for */
to_network_layer(&r.info);
/* pass the data to the network layer */
inc(frame_expected);
/* next time expect the other sequence nr */
}
s.ack = 1 − frame_expected;
/* tell which frame is being acked */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* send acknowledgement */
}
}
}
|
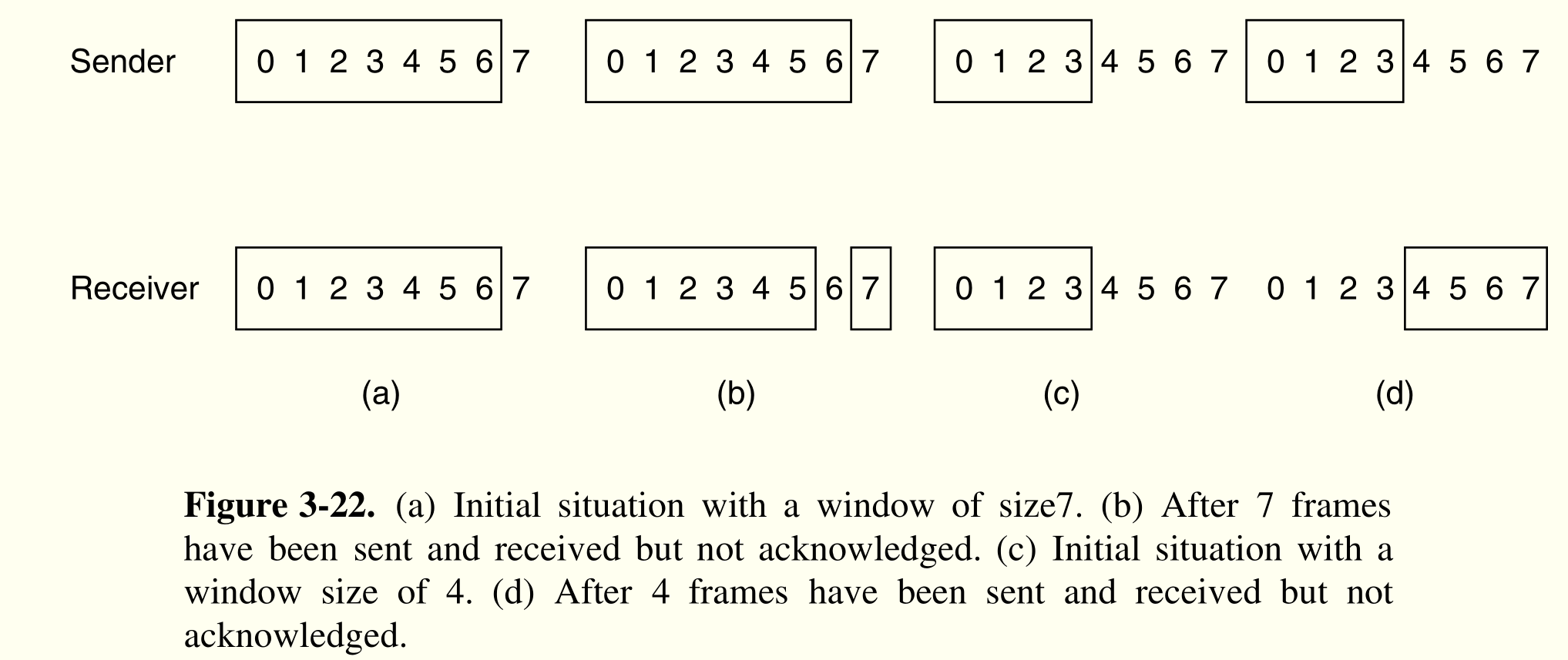
滑动窗口协议¶
双工,而不是使用两个单工协议。
piggybacking
捎带确认,不单独发送确认帧,而是把确认信息放在下一数据帧当中
使用 sending window 和 receiving window。窗口数目对应帧所需缓存区大小
- sending window
- 窗口中保存需要发送的帧
- 新到的帧窗口扩张
- 收到确认后,窗口缩小
- receiving window
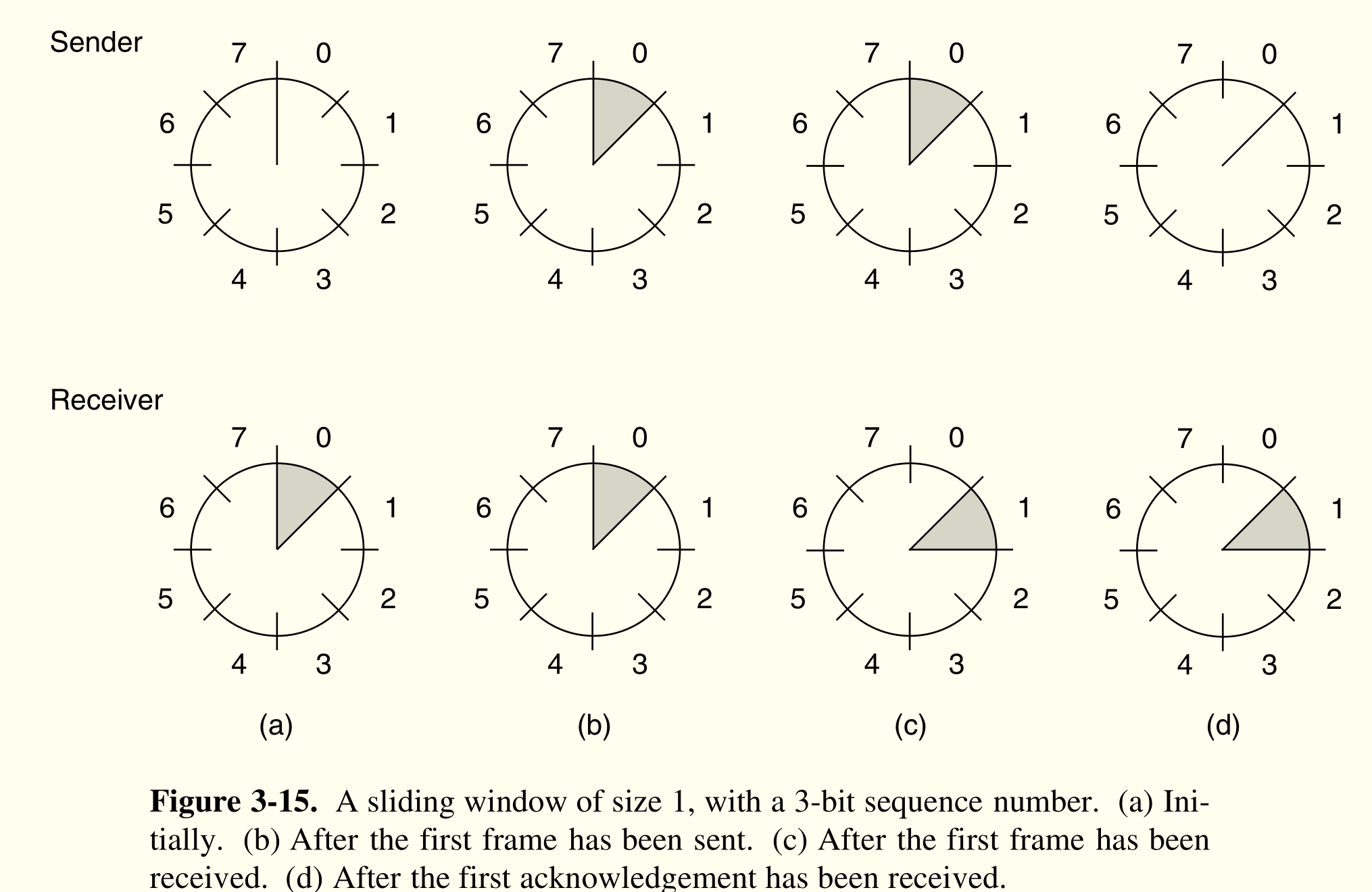
1 位 滑动窗口¶
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
| /* Protocol 4 (Sliding window) is bidirectional. */
#define MAX_SEQ 1
/* must be 1 for protocol 4 */
typedef enum {frame_arrival, cksum_err, timeout} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
void protocol4 (void)
{
seq_nr next_frame_to_send;
/* 0 or 1 only */
seq_nr frame_expected;
/* 0 or 1 only */
frame r, s;
/* scratch variables */
packet buffer;
/* current packet being sent */
event_type event;
next_frame_to_send = 0;
/* next frame on the outbound stream */
frame_expected = 0;
/* frame_expected next */
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* fetch a packet from the network layer */
s.info = buffer;
/* prepare to send the initial frame */
s.seq = next_frame_to_send;
/* insert sequence number into frame */
s.ack = 1 − frame_expected;
/* piggybacked ack */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* transmit the frame */
start_timer(s.seq);
/* start the timer running */
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* frame_arrival, cksum_err, or timeout */
if (event == frame_arrival) {
/* a frame has arrived undamaged */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* go get it */
if (r.seq == frame_expected) {
/* handle inbound frame stream */
to_network_layer(&r.info);
/* pass packet to_network_layer */
inc(frame_expected);
/* invert seq number expected next */
}
if (r.ack == next_frame_to_send) {
/* handle outbound frame stream */
stop_timer(r.ack);
/* turn the timer off */
from_network_layer(&buffer);
/* fetch new pkt from_network_layer */
inc(next_frame_to_send);
/* invert sender’s sequence number */
}
}
s.info = buffer;
/* construct outbound frame */
s.seq = next_frame_to_send;
/* insert sequence number into it */
s.ack = 1 − frame_expected;
/* seq number of last received frame */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* transmit a frame */
start_timer(s.seq);
/* start the timer running */
}
}
|
多位窗口¶
由于信道传输时间不可忽略,1 位滑动窗口的异常启动问题不可忽略,需要提高带宽利用率。
bandwidth-delya product
$\text{带宽(bits/sec)}\times \text{单次传输时间}$
在以帧数为单位时,记作 BD
在阻塞前,一次性发送$w=2BD+1$。如果考虑发送方连续发送帧并且在往返时间内收到一个确认,那么两倍的带宽-延时就是发送方可以连续发送的帧的个数;$+1$是因为必须接收完整个帧之后确认帧才会被发出。pipelining (排队发送帧)就能提高链路利用率。
$$\text{link utilization}=\frac{w}{1+2BD}$$
- go-back-n:放弃出错帧之后的正确帧(相当于窗口大小 1)
- selective repeat,只放弃错误帧,缓存之后的正确帧
两种策略分别平衡缓存区和带宽利用率。
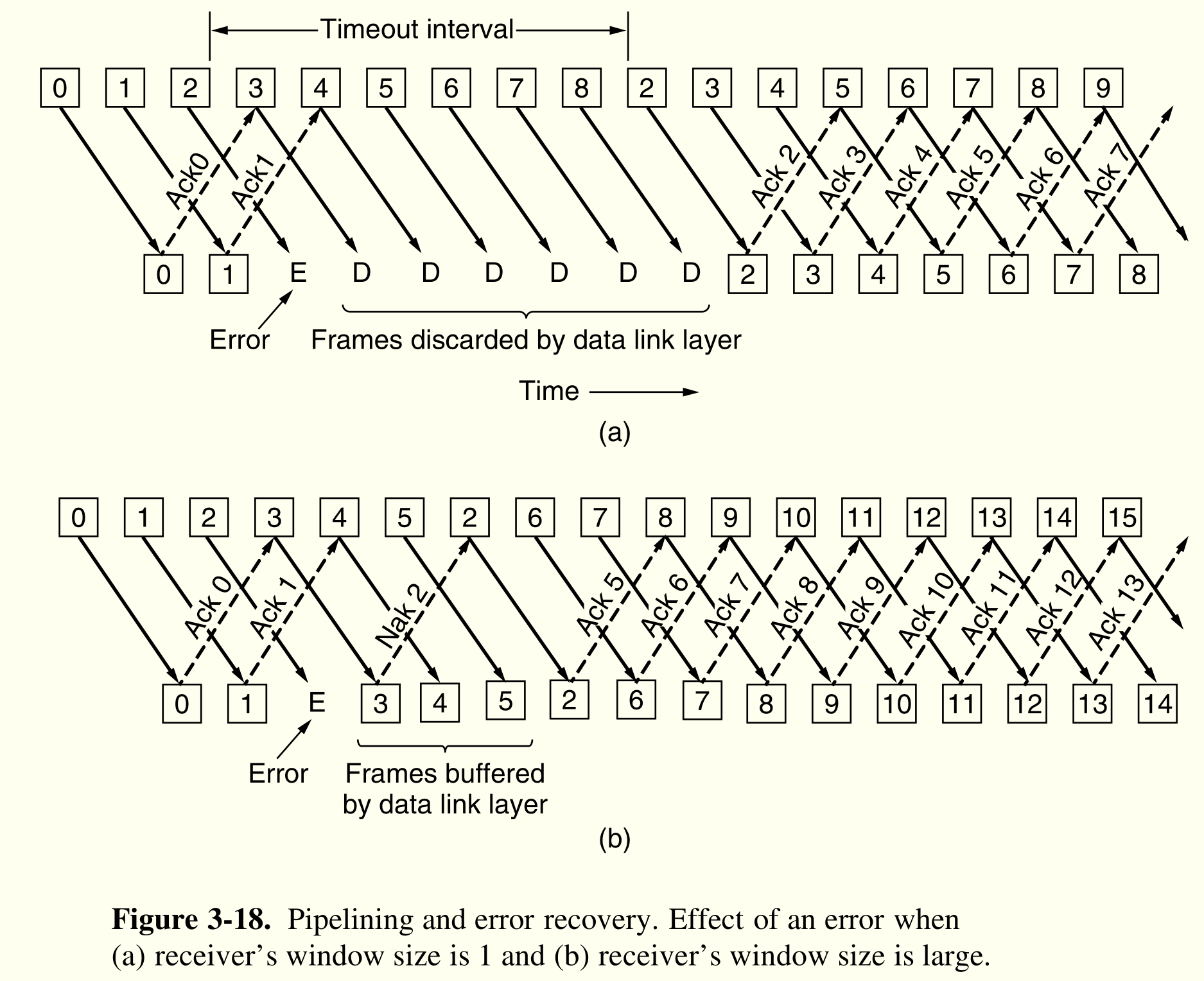
Go-Back-N 回退 N 协议¶
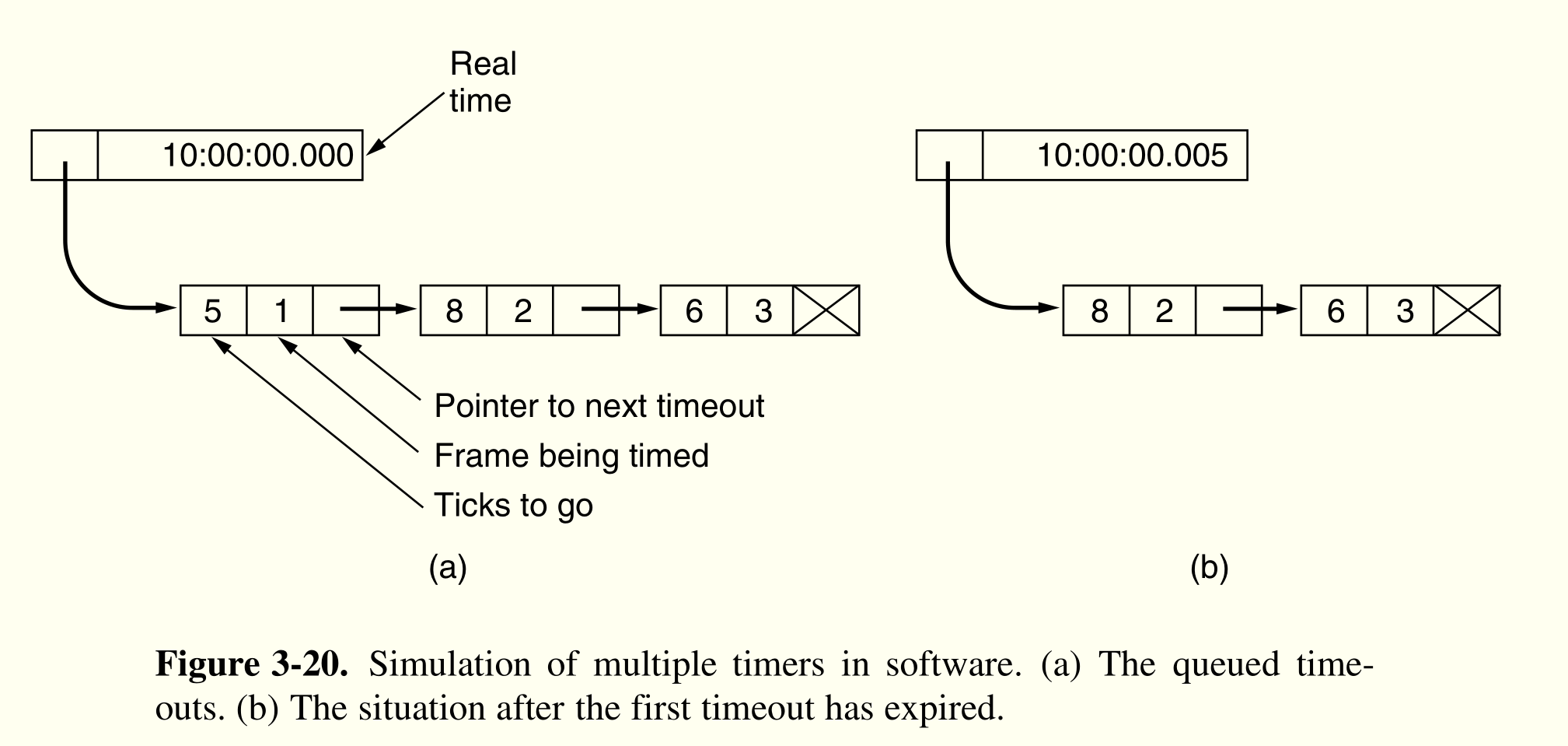
最多发送$MAX\_SEQ$个帧。虽然不需要缓存出错后到来的帧,但是它也没有因此完全摆脱缓存问题。由于发送方可能在将来的某个时刻要重传所有未被确认的帧,所以,它必须把已经发送出去的帧一直保留,直到它能肯定接收方已经接受了这些帧。对之前的帧,可以用软件模拟每个帧的时间计数器
cumulative acknowledgement
累计确认,当$n$号帧到达,之前序号的帧自动被确认(因为回退特性)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
| /* Protocol 5 (Go-back-n) allows multiple outstanding frames. The sender may transmit up
to MAX_SEQ frames without waiting for an ack. In addition, unlike in the previous
protocols, the network layer is not assumed to have a new packet all the time. Instead,
the network layer causes a network layer ready event when there is a packet to send. */
#define MAX_SEQ 7
typedef enum {frame_arrival, cksum_err, timeout, network_layer_ready} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
static boolean between(seq_nr a, seq_nr b, seq_nr c)
{
/* Return true if a <= b < c circularly; false otherwise. */
if (((a <= b) && (b < c)) || ((c < a) && (a <= b)) || ((b < c) && (c < a)))
return(true);
else
return(false);
}
static void send_data(seq_nr frame_nr, seq_nr frame_expected, packet buffer[ ])
{
/* Construct and send a data frame. */
frame s;
/* scratch variable */
s.info = buffer[frame_nr];
/* insert packet into frame */
s.seq = frame_nr;
/* insert sequence number into frame */
s.ack = (frame_expected + MAX_SEQ) % (MAX_SEQ + 1);/* piggyback ack */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* transmit the frame */
start_timer(frame_nr);
/* start the timer running */
}
void protocol5(void)
{
seq_nr next_frame_to_send;
/* MAX_SEQ > 1; used for outbound stream */
seq_nr ack_expected;
/* oldest frame as yet unacknowledged */
seq_nr frame_expected;
/* next frame_expected on inbound stream */
frame r;
/* scratch variable */
packet buffer[MAX_SEQ + 1];
/* buffers for the outbound stream */
seq_nr nbuffered;
/* number of output buffers currently in use */
seq_nr i;
/* used to index into the buffer array */
event_type event;
enable_network_layer();
/* allow network layer ready events */
ack_expected = 0;
/* next ack_expected inbound */
next_frame_to_send = 0;
/* next frame going out */
frame_expected = 0;
/* number of frame_expected inbound */
nbuffered = 0;
/* initially no packets are buffered */
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* four possibilities: see event_type above */
switch(event) {
case network_layer_ready:
/* the network layer has a packet to send */
/* Accept, save, and transmit a new frame. */
from_network_layer(&buffer[next_frame_to_send]); /* fetch new packet */
nbuffered = nbuffered + 1;
/* expand the sender’s window */
send_data(next_frame_to_send, frame_expected, buffer);/* transmit the frame */
inc(next_frame_to_send);
/* advance sender’s upper window edge */
break;
case frame_arrival:
/* a data or control frame has arrived */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* get incoming frame from_physical_layer */
if (r.seq == frame_expected) {
/* Frames are accepted only in order. */
to_network_layer(&r.info);
/* pass packet to_network_layer */
inc(frame_expected);
/* advance lower edge of receiver’s window */
}
/* Ack n implies n − 1, n − 2, etc. Check for this. */
while (between(ack_expected, r.ack, next_frame_to_send)) {
/* Handle piggybacked ack. */
nbuffered = nbuffered − 1;
/* one frame fewer buffered */
stop_timer(ack_expected);
/* frame arrived intact; stop_timer */
inc(ack_expected);
/* contract sender’s window */
}
break;
case cksum_err: break;
/* just ignore bad frames */
case timeout:
/* trouble; retransmit all outstanding frames */
next_frame_to_send = ack_expected;
/* start retransmitting here */
for (i = 1; i <= nbuffered; i++) {
send_data(next_frame_to_send, frame_expected, buffer);/* resend_frame */
inc(next_frame_to_send);
/* prepare to send the next one */
}
}
if (nbuffered < MAX_SEQ)
enable_network_layer();
else
disable_network_layer();
}
}
|
selective repeat 选择重传¶
针对错误更加频繁的情景。窗口移动后,和老的不重叠,防止老的重传和新的帧混淆。$\frac{(MAX\_SEQ+1)}{2}$。启用一个辅助计时器,在没有反向数据帧时候单独发出确认帧。
NAK
negative acknowledgement,否认确定记号。触发某一帧的重传
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
| /* Protocol 6 (Selective repeat) accepts frames out of order but passes packets to the
network layer in order. Associated with each outstanding frame is a timer. When the timer
expires, only that frame is retransmitted, not all the outstanding frames, as in protocol 5. */
#define MAX_SEQ 7
/* should be 2ˆn − 1 */
#define NR_BUFS ((MAX_SEQ + 1)/2)
typedef enum {frame_arrival, cksum_err, timeout, network_layer_ready, ack_timeout} event_type;
#include "protocol.h"
boolean no_nak = true;
/* no_nak has been sent yet */
seq_nr oldest_frame = MAX_SEQ + 1;
/* initial value is only for the simulator */
static boolean between(seq_nr a, seq_nr b, seq_nr c)
{
/* Same as between in protocol 5, but shorter and more obscure. */
return ((a <= b) && (b < c)) || ((c < a) && (a <= b)) || ((b < c) && (c < a));
}
static void send_frame(frame_kind fk, seq_nr frame_nr, seq_nr frame_expected, packet buffer[ ])
{
/* Construct and send a data, ack, or nak frame. */
frame s;
/* scratch variable */
s.kind = fk;
/* kind == data, ack, or nak */
if (fk == data)
s.info = buffer[frame_nr % NR_BUFS];
s.seq = frame_nr;
/* only meaningful for data frames */
s.ack = (frame_expected + MAX_SEQ) % (MAX_SEQ + 1);
if (fk == nak)
no_nak = false;
/* one nak per frame, please */
to_physical_layer(&s);
/* transmit the frame */
if (fk == data)
start_timer(frame_nr % NR_BUFS);
stop_ack_timer();
/* no need for separate ack frame */
}
void protocol6(void)
{
seq_nr ack_expected;
/* lower edge of sender’s window */
seq_nr next_frame_to_send;
/* upper edge of sender’s window + 1 */
seq_nr frame_expected;
/* lower edge of receiver’s window */
seq_nr too far;
/* upper edge of receiver’s window + 1 */
int i;
/* index into buffer pool */
frame r;
/* scratch variable */
packet out_buf[NR_BUFS];
/* buffers for the outbound stream */
packet in_buf[NR_BUFS];
/* buffers for the inbound stream */
boolean arrived[NR_BUFS];
/* inbound bit map */
seq_nr nbuffered;
/* how many output buffers currently used */
event_type event;
enable_network_layer();
/* initialize */
ack_expected = 0;
/* next ack_expected on the inbound stream */
next_frame_to_send = 0;
/* number of next outgoing frame */
frame_expected = 0;
too_far = NR_BUFS;
nbuffered = 0;
/* initially no packets are buffered */
for (i = 0; i < NR_BUFS; i++) arrived[i] = false;
while (true) {
wait_for_event(&event);
/* five possibilities: see event_type above */
switch(event) {
case network_layer_ready:
/* accept, save, and transmit a new frame */
nbuffered = nbuffered + 1;
/* expand the window */
from_network_layer(&out_buf[next_frame_to_send % NR_BUFS]); /* fetch new packet */
send_frame(data, next_frame_to_send, frame_expected, out_buf);/* transmit the frame */
inc(next_frame_to_send);
/* advance upper window edge */
break;
case frame_arrival:
/* a data or control frame has arrived */
from_physical_layer(&r);
/* fetch incoming frame from_physical_layer */
if (r.kind == data) {
/* An undamaged frame has arrived. */
if ((r.seq != frame_expected) && no_nak)
send_frame(nak, 0, frame_expected, out_buf);
else
start_ack_timer();
if (between(frame_expected,r.seq,too far) && (arrived[r.seq%NR_BUFS]==false)) {
/* Frames may be accepted in any order. */
arrived[r.seq % NR_BUFS] = true;
/* mark buffer as full */
in_buf[r.seq % NR_BUFS] = r.info;
/* insert data into buffer */
while (arrived[frame_expected % NR_BUFS]) {
/* Pass frames and advance window. */
to_network_layer(&in_buf[frame_expected % NR_BUFS]);
no_nak = true;
arrived[frame_expected % NR_BUFS] = false;
inc(frame_expected);
/* advance lower edge of receiver’s window */
inc(too far);
/* advance upper edge of receiver’s window */
start_ack_timer();
/* to see if a separate ack is needed */
}
}
}
if((r.kind==nak) && between(ack_expected,(r.ack+1)%(MAX_SEQ+1),next_frame_to_send))
send_frame(data, (r.ack+1) % (MAX_SEQ + 1), frame_expected, out_buf);
while (between(ack_expected, r.ack, next_frame_to_send)) {
nbuffered = nbuffered − 1;
/* handle piggybacked ack */
stop_timer(ack_expected % NR_BUFS);
/* frame arrived intact */
inc(ack_expected);
/* advance lower edge of sender’s window */
}
break;
case cksum_err:
if (no_nak)
send_frame(nak, 0, frame_expected, out_buf); /* damaged frame */
break;
case timeout:
send_frame(data, oldest_frame, frame_expected, out_buf); /* we timed out */
break;
case ack_timeout:
send_frame(ack,0,frame_expected, out_buf);
/* ack timer expired; send ack */
}
if (nbuffered < NR_BUFS)
enable_network_layer();
else
disable_network_layer();
}
}
|
ch4 介质访问控制子层¶
MAC
Medium Access Control
在多用户之间分配单广播信道。FDM(频分复用)效率不高。信道速度 $C \rm{bps}$ ,每帧 $1/\mu\rm{bit}$ ,帧到达速度 $\lambda\rm{frames/sec}$ 。实际延时
$$T=\frac{1}{\mu C -\lambda}$$
如果信道等分 $N$ 份,延时大幅度增加。因此需要动态分配信道
$$T_N=\frac{1}{\mu (C/N) -(\lambda/N)}=\frac{N}{\mu C -\lambda}=NT$$
- 流量独立,在 $\Delta_t$ 时间间隔中,帧数期望为 $\lambda\Delta_t$ (假定是泊松分布,而暂时不考虑突发流量)
- 单信道,核心,没有其他外部手段通信/核对信息
- 冲突可观察
- 时间连续/分槽 slotted
- 载波侦听 carrirer sense 或不听
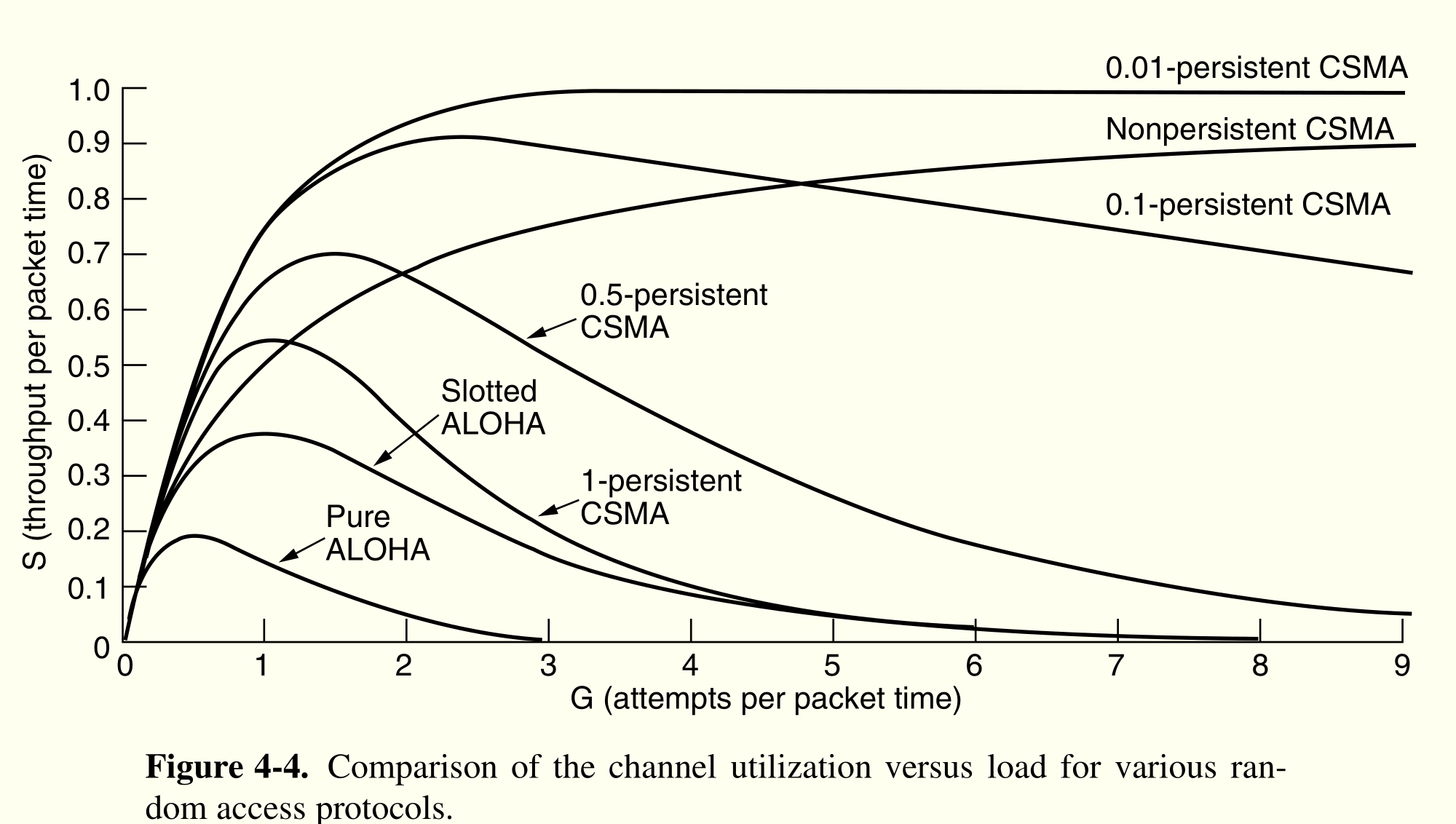
多路访问协议¶
contention system
竞争系统:共享信道,被同时发送帧而都失效
ALOHA¶
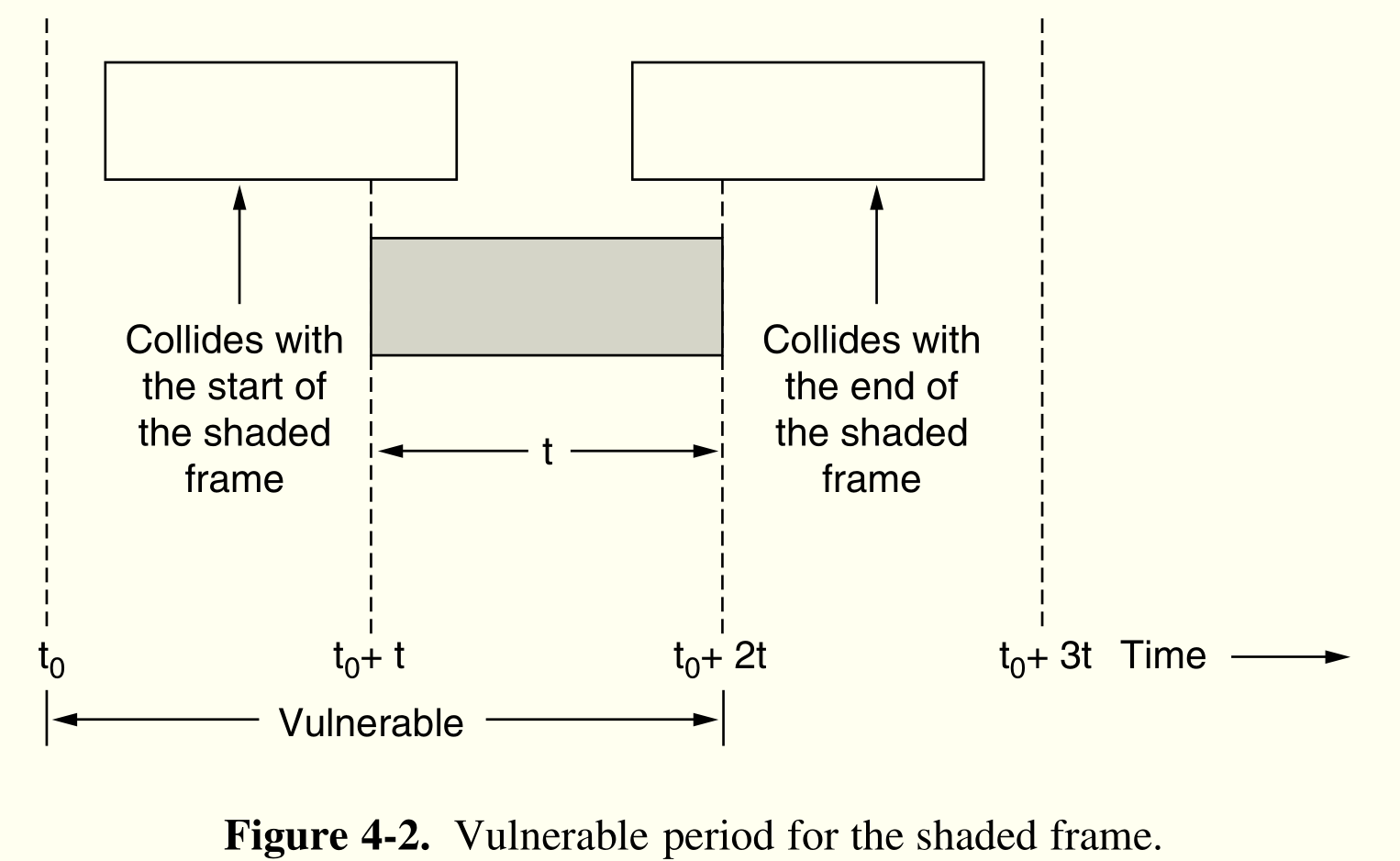
有数据直接发,如果碰撞,在等待随机时间之后重发。
假设帧等长,发送用时$t$,帧产生服从泊松分布,一个“帧时”平均有 G 帧,实际产生 k 帧概率为
$$\mathrm{Pr[k]}=\frac{G^ke^{-G}}{k!}$$
一帧在$2t$中任意有 1 帧产生都会损毁,因此吞吐量最终为
$$S=Ge^{-2G}$$
分槽 ALOHA¶
要求每帧必须在时间槽开始时才能尝试发送,不能在任意时刻发送,只需要考虑单槽$t$内的碰撞。吞吐量
$$S=Ge^{-G}$$
1 帧需要 k 次尝试的几率为
$$P_k=e^{-G}(1-e^{-G})^{k-1}$$
传输次数期望为
$$E=\sum kP_k=\sum ke^{-G}(1-e^{-G})^{k-1}=e^G$$
CSMA¶
CSMA
Carrier Sense Multiple Access,载波侦听多路访问协议
在发送自己帧之前,监听是否信道被占用,不占用再发送;如果占用
Persistent:等到占用结束直接开始发¶
会在同时多站等发时候冲突
Nonpersistent¶
等待一段时间后再检测
p-persistent¶
针对分槽时间,每个槽如果空闲,以$p$的概率发,$1-p$的概率等下个时间槽。
如果有 k 个站需要传数据,站得发送的概率$P$为
$$P=kp(1-p)^{k-1}$$
在$p=\frac{1}{k}$时候有$P_\max$为
$$P_\max=(\frac{k-1}{k})^{k-1}$$
而且$k\to\infty$时候有$P\to\frac{1}{e}$。
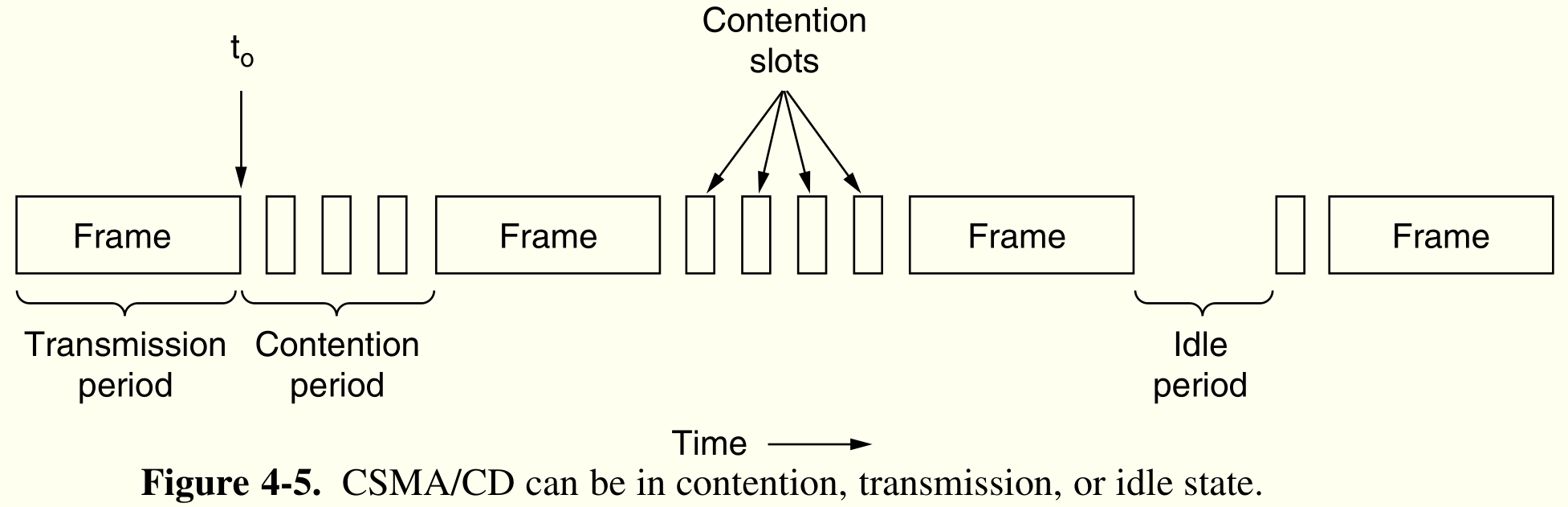
CSMA/CD collision detection¶
在发送前,信道空闲时候,发送竞争信号,竞争胜利者发送数据帧
CSMA/CA collision avoidance¶
binary exponential backoff
二进制指数后退。在$i$次碰撞后,在p-persistent CSMA基础上改为等待$0\sim2^i-1$个时间槽
实际中,有时间槽次数上限和碰撞次数上限
竞争时间间隔为$j$的概率
$$P_{t=jT_0}=P(1-P)^{j-1}$$
每次竞争平均时间槽数为
$$E=\sum_{j=0} jP(1-P)^{j-1}=\frac{1}{P}$$
Bit-Map 位图协议 无冲突¶
信道中有公共信息广播时间。在该时间里,每个站有一个槽,发送信息表示接下来需要发送数据帧;沉默表示接下来不发。然后站按照申请的结果发。平均等待$N$个槽时间
token ring 令牌环 无冲突¶
所有站连接成一个单环结构,传递令牌。得到令牌的发数据,发完继续传;如果不用发数据直接向下传
binary countdown 二进制计数 无冲突¶
信道中有公共信息广播时间,所有站监听。如果需要发数据,从高位开始,在对应时间槽中发送自己优先级(唯一,二进制表示)消息,消息之间是或关系。只有知道自己是优先级最高的才能接下来发送。竞争用时$\log_2N$
The Adaptive Tree Walk Protocol 自适应树遍历协议¶
注意到,如果竞争站的数目$k$比较小时候,p-persistent CSMA 的获得信道概率会上升。因此可以通过分组减少竞争,极大提升信道使用效果
自适应树中,将站看作是二叉树的叶节点,从根节点开始搜索。如果某个节点冲突,向下探寻左、右子节点;如果左节点不冲突了,给左节点下需求站发送数据;下一时间槽给右节点的站。在公共广播期间,站按照自身的父节点被搜索到的顺序竞争时间槽。
如果$q$个站随机均匀分布,在让每个槽中参与竞争的平均站数为 1 时,得到最优树高$1+\log_2q$
以太网¶
| hub 集线器 | switch 交换机 |
|---|
| pro | 易排错 | 扩容;无冲突;安全 |
| con | 不能扩容,逻辑上等同单线缆 | 自带 buffer 防止同时发送端口 |
ch5 网络层¶
- 向上提供的服务应该独立于路由器技术
- 应该向传输层屏蔽路由器的数量、类型和拓扑关系
- 传输层可用的网络地址应该有一个统一编址方案,甚至可以跨越 LAN 和 WAN
datagram
数据报网络,所有的数据包都被独立地注入到网络中,并且每个数据包独立路由,不需要提前建立任何设置
virtual circuit
虚电路网络,在发送数据包之前,必须首先建立起一条从源路由器到目标路由器之间的路径
| datagram | virtual-circuit |
|---|
| 线路初始化 | 不需要 | 需要 |
| 寻址 | 包带有源和目标地址 | 包带有短 VC 号 |
| 状态信息 | 路由不包含连接信息 | 每条虚电路(VC)需要路由记录每个连接 |
| 路由 | 每个包单独路由 | VC 设置时候路由,包遵守 |
| 路由失效影响 | 无,除了因为崩溃丢的包 | 故障路由相关 VC 均中断 |
| 服务质量 | 困难 | 简单,如果建立 VC 时候资源足够 |
| 拥塞控制 | 困难 | 简单,如果建立 VC 时候资源足够 |
路由算法¶
routing algorithm
路由算法。网络层软件决定入境数据包在哪条线外发
optimality principle
路由最优化原理。如果路由 J 在 I 到 K 最优路径,那么 J 到 K 最优路径也是同样的路由
sink tree
汇集树。从所有的源到一个指定目标的最优路径的集合构成了一棵以目标节点为根的树/DAG(有向无环图)
spanning tree
包含所有路由器的树,不一定是最优路径(和汇集树相区别)
Dijstra 最短路径¶
每次找到距离源距离最近(距离=到已发现集合的某点距离+该点距离源距离)的新节点,加入发现集合
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| #define MAX_NODES 1024
/* maximum number of nodes */
#define INFINITY 1000000000
/* a number larger than every maximum path */
int n, dist[MAX_NODES][MAX_NODES];
/* dist[i][j] is the distance from i to j */
void shortest path(int s, int t, int path[])
{
struct state {
/* the path being worked on */
int predecessor;
/* previous node */
int length;
/* length from source to this node */
enum {permanent, tentative} label;
/* label state */
} state[MAX_NODES];
int i, k, min;
struct state *p;
for (p = &state[0]; p < &state[n]; p++) {
/* initialize state */
p->predecessor = −1;
p->length = INFINITY;
p->label = tentative;
}
state[t].length = 0; state[t].label = permanent;
k = t;
/* k is the initial working node */
do {
/* Is there a better path from k? */
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){ //n node
if (dist[k][i] != 0 && state[i].label == tentative) {
if (state[k].length + dist[k][i] < state[i].length) {
state[i].predecessor = k;
state[i].length = state[k].length + dist[k][i];
}
}
}
/* Find the tentatively labeled node with the smallest label. */
k = 0; min = INFINITY;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (state[i].label == tentative && state[i].length < min) {
min = state[i].length;
k = i;
}
}
state[k].label = permanent;
} while (k != s);
/* Copy the path into the output array. */
i = 0; k = s;
do {path[i++] = k; k = state[k].predecessor; } while (k >= 0);
}
|
flooding 泛洪¶
每一个入境数据包发送到除了该数据包到达的那条线路以外的每条出境线路
- 泛洪包带有寿命,计数减到 0 之后不再发
- 追踪泛洪包防止二次发送。泛洪包带序号,一个序号对应一次泛洪,一次泛洪只发送一次
distance vector routing 距离向量路由¶
每个路由器维护一张表(即一个矢量),表中列出了当前已知的到每个目标的最佳距离,以及所使用的链路。这些表通过邻居之间相互交换信息而不断被更新,最终每个路由器都了解到达每个目的地的最佳链路。
又名 Bellman-Fold 算法
Count-to-Infinity
无穷计数问题。坏消息传递慢,距离每次增 1 而已(没有一个路由器具有一个比它所有邻居的最小值还大于 1 的值,从邻居获得道路信息不包含自身是否在道路上)
link state routing 链路状态路由¶
- 发现它的邻居节点,并了解其网络地址
- 设置到每个邻居节点的距离或者成本度量值
- 构造一个包含所有刚刚获知的链路信息包
- 将这个包发送给所有其他的路由器,并接收来自所有其他路由器的信息包
- 计算出到每个其他路由器的最短路径
每个路由都知道网络拓扑结构,每个路由自行完成Dijstra 最短路径算法
层次路由¶
分层。可以证明对于 $N$ 路由数目网络最优层数 $\ln N$,每个路由器查找表条目 $e\ln N$。
广播路由¶
multidestination routing
多目标路由。每个数据包包含一组目标地址,路由对于某条线上转发时候只保留线连接区域地址,直到只发给 1 个目标地址
reverse path forwarding
逆向路径转发。检测数据包是否来自汇集树(或者放宽为优化的生成树),否则丢弃,结合泛洪
- 每个路由单独发包
- 泛洪
- 多目标路由
组播路由¶
core-based tree
基于核心树。只对核心(core/root)建生成树
- 干脆 广播路由
- 修建生成树,按需要传播
- 其他路由先发到核心,核心走核心树
anycast routing 选播路由¶
anycast
数据包发送到特定一个组中最近的一个路由
拥塞控制算法¶
bufferfloat
路由内存充足反而容易导致拥塞。数据包(本来会因为内存不足丢弃)排到队列前面时,它们早己经超时(重复地)并且它们的副本也己经发送
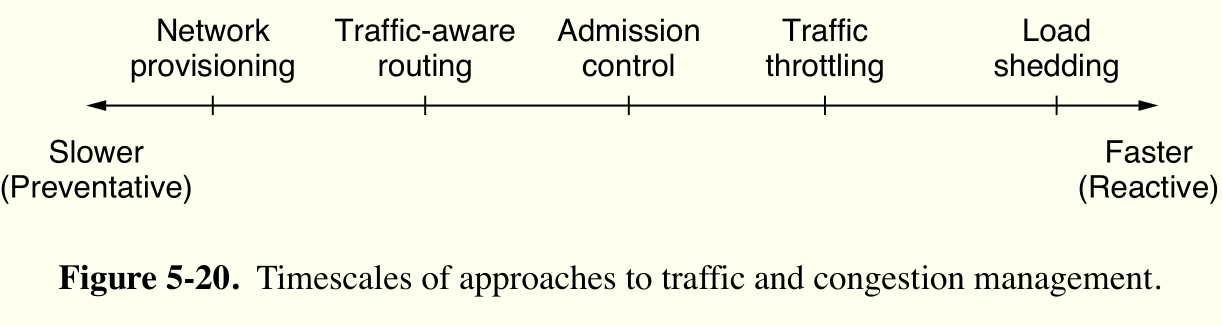
Traffic-Aware Routing¶
流量感知路由。将负载考虑到路由选择上,但不能直接使用流量调整,防止路由选择波动。
admission control¶
准入控制。只能针对虚电路网络,在可承担负载情况下才建立新连接。
load shedding¶
负载脱落。直接抛弃负载保证不拥塞。抛弃优先级可以结合流量费用设定。
wine
旧数据包保留:如文件传输
milk
新数据包保留:如流媒体
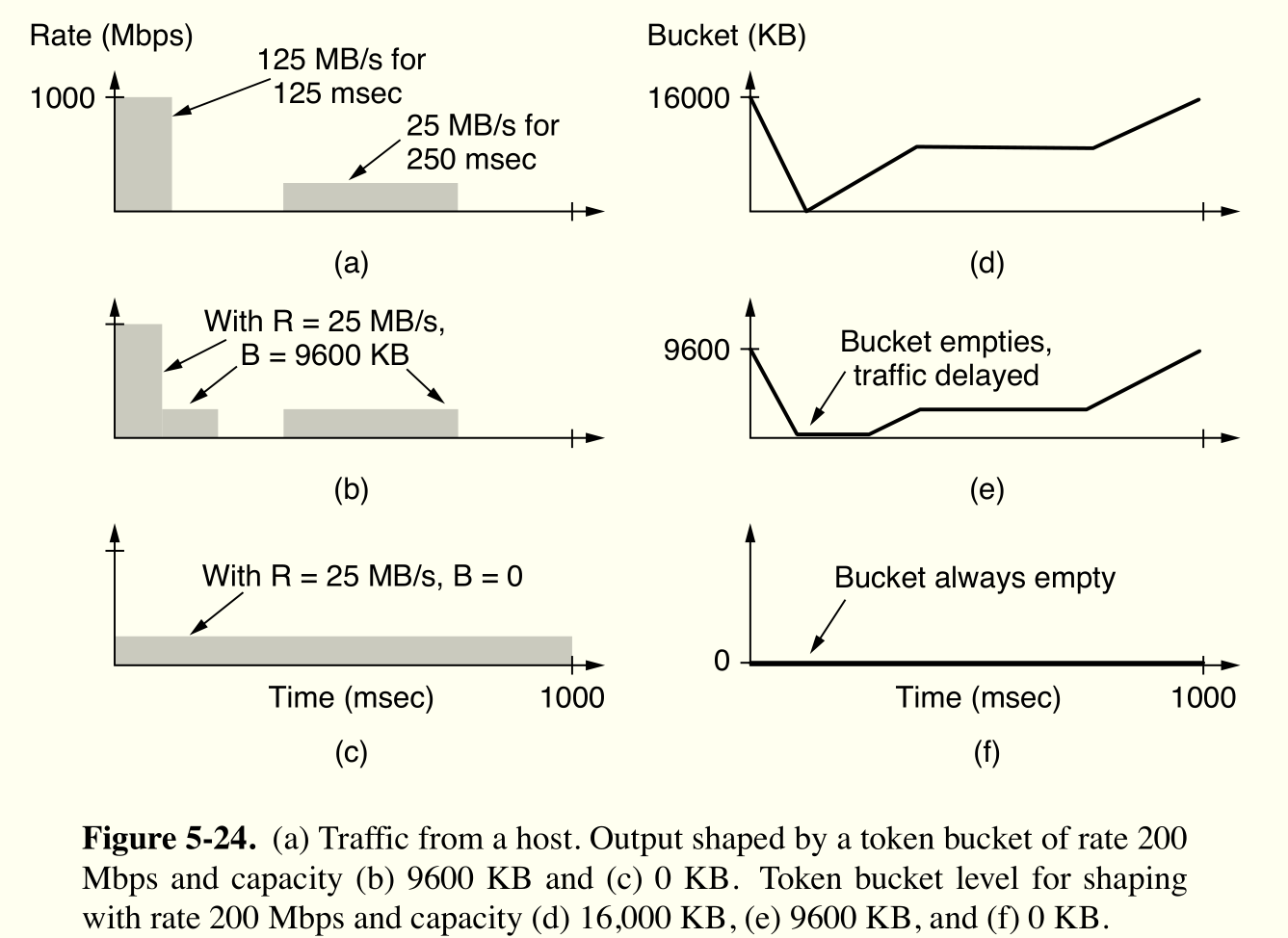
traffic shaping¶
流量整形。
桶容量 $B$ ,数据速率 $R$
leaky bucket
漏桶。向缓冲区发包,包以 $R$ 离开缓冲区
token bucket
令牌桶。令牌以 $R$ 速度累计, 得到令牌才能发包
流量突发时长 $S$ ,突发产生速率 $M$ ,则桶算法有
$$B+RS=MS$$
还可以级联桶,调控平均速率和突发最大速率。
active queue management 主动队列管理¶
主动管理负载避免拥塞,路由监控自己使用的资源。期待延迟为 $d$ ,队列长度 $s$ ,有关系式
$$d_{new}=\alpha d_{old}+(1-\alpha)s$$
Exponentially Weighted Moving Average
EWMA,指数加权移动平均。 $\alpha$ 是路由遗忘历史信息的常数。等同于低通滤波器。 期待延迟 $d$ 超过阈值预示拥塞发生
Random Early Detection 随机早期检测¶
RED。因为路由难以得到显式信息通知拥塞,只有包丢失是容易感知的,但是包丢失对于避免拥塞太晚了。当某条链路上的平均队列长度超过某个阈值时,该链路就被认为即将拥塞,因此路由器随机丢弃一小部分数据包。隐含传递拥塞信号
choke packets¶
直接向发送方回传拥塞发生的通知数据包。
Explicit Congestion Notification 显式拥塞通知¶
ECN。不单独发拥塞通知包,在包中间标志位标记拥塞信息。
Hop-by-Hop Backpressure¶
防止路程过长,拥塞通知延迟太久。同时用choke packets(拥塞通知包)通知中间路由控制流量。
ch6 传输层¶
传输层主要跑在用户机上,而网络层跑在路由器上
Socket¶
| 原语 | 含义 |
|---|
| socket | 建立一个新通讯端点 |
| bind | 将 socket 与一个本地地址关联 |
| listen | 声明愿意接受连接;给出队列长度 |
| accept | 被动创建一个入境连接 |
| connect | 主动尝试创建连接 |
| send | 通过连接传输数据 |
| receive | 通过连接接受数据 |
| close | 断开连接 |
文件传输程序¶
客户端¶
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
| /* This page contains a client program that can request a file from the server program
* on the next page. The server responds by sending the whole file.
*/
#include <netdb.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 8080
/* arbitrar y, but client & server must agree */
#define BUF_SIZE 4096
/* block transfer size */
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int c, s, bytes;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
/* buffer for incoming file */
struct hostent* h;
/* info about server */
struct sockaddr in_channel;
/* holds IP address */
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: client server-name file-name");
exit(-1);
}
h = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
/* look up host’s IP address */
if (!h)
{
printf("gethostbyname failed to locate %s", argv[1]);
exit(-1);
}
s = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (s < 0)
{
printf("socket call failed");
exit(-1);
}
memset(&channel, 0, sizeof(channel));
channel.sin_family = AF_INET;
memcpy(&channel.sin_addr.s_addr, h->h_addr, h->h_length);
channel.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
c = connect(s, (struct sockaddr*)&channel, sizeof(channel));
if (c < 0)
{
printf("connect failed");
exit(-1);
}
/* Connection is now established. Send file name including 0 byte at end. */
write(s, argv[2], strlen(argv[2]) + 1);
/* Go get the file and write it to standard output. */
while (1)
{
bytes = read(s, buf, BUF_SIZE);
/* read from socket */
if (bytes <= 0)
exit(0);
/* check for end of file */
write(1, buf, bytes);
/* wr ite to standard output */
}
}
|
服务器端¶
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
| #include <sys/types.h>
/* This is the server code */
#include <netdb.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 8080
/* arbitrar y, but client & server must agree */
#define BUF_SIZE 4096
/* block transfer size */
#define QUEUE_SIZE 10
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int s, b, l, fd, sa, bytes, on = 1;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
/* buffer for outgoing file */
struct sockaddr_in channel;
/* holds IP address */
/* Build address structure to bind to socket. */
memset(&channel, 0, sizeof(channel));
/* zero channel */
channel.sin_family = AF_INET;
channel.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
channel.sin + port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
/* Passive open. Wait for connection. */
s = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
/* create socket */
if (s < 0)
{
printf("socket call failed");
exit(-1);
}
setsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, (char*)&on, sizeof(on));
b = bind(s, (struct sockaddr*)&channel, sizeof(channel));
if (b < 0)
{
printf("bind failed");
exit(-1);
}
l = listen(s, QUEUE_SIZE);
/* specify queue size */
if (l < 0)
{
printf("listen failed");
exit(-1);
}
/* Socket is now set up and bound. Wait for connection and process it. */
while (1)
{
sa = accept(s, 0, 0);
/* block for connection request */
if (sa < 0)
{
printf("accept failed");
exit(-1);
}
read(sa, buf, BUF_SIZE);
/* read file name from socket */
/* Get and return the file. */
fd = open(buf, O_RDONLY);
/* open the file to be sent back */
if (fd < 0)
{
printf("open failed");
}
while (1)
{
bytes = read(fd, buf, BUF_SIZE); /* read from file */
if (bytes <= 0)
break;
/* check for end of file */
write(sa, buf, bytes);
/* wr ite bytes to socket */
}
close(fd);
/* close file */
close(sa);
/* close connection */
}
}
|













